5 Essential Tips for Cloud Computing Security
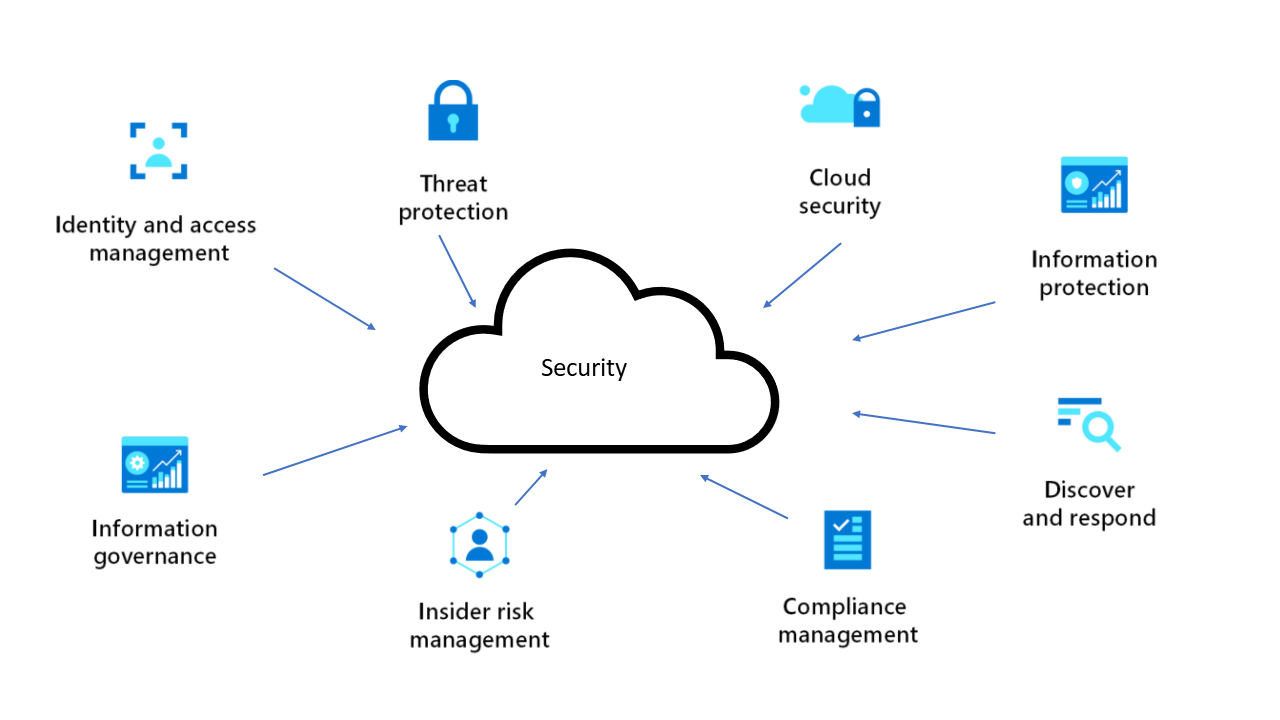
The Imperative of Cloud Computing Security
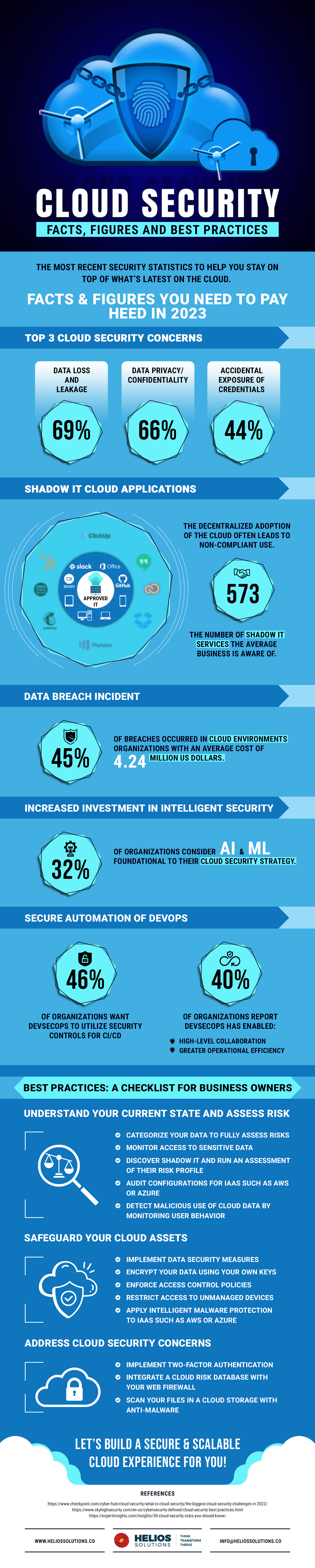
In today's digital landscape, cloud computing has revolutionized the way organizations operate. From small startups to large enterprises, the shift towards cloud storage and services has brought with it tremendous benefits like scalability, flexibility, and reduced infrastructure costs. However, with these advantages comes the critical responsibility of ensuring cloud security. This blog post explores five essential tips that organizations should implement to fortify their cloud computing environments against cyber threats.

1. Robust Identity and Access Management
The first line of defense in securing any cloud infrastructure is through Identity and Access Management (IAM). Here's how you can strengthen IAM:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to add an additional layer of security, requiring users to present two or more verification factors before gaining access.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on the roles within the organization to ensure users have just enough access to perform their tasks without unnecessary privileges.
- Regular Access Reviews: Conduct periodic reviews to verify that access rights are still relevant and adjust as needed, especially after an employee leaves or changes roles.
Implementing IAM Best Practices
To maximize security through IAM:
- Use strong password policies and enforce password rotation.
- Utilize privileged access management (PAM) for high-level accounts.
- Ensure that all access is logged for auditing purposes.
🔒 Note: Regularly update your IAM policies in response to organizational changes or security incidents.
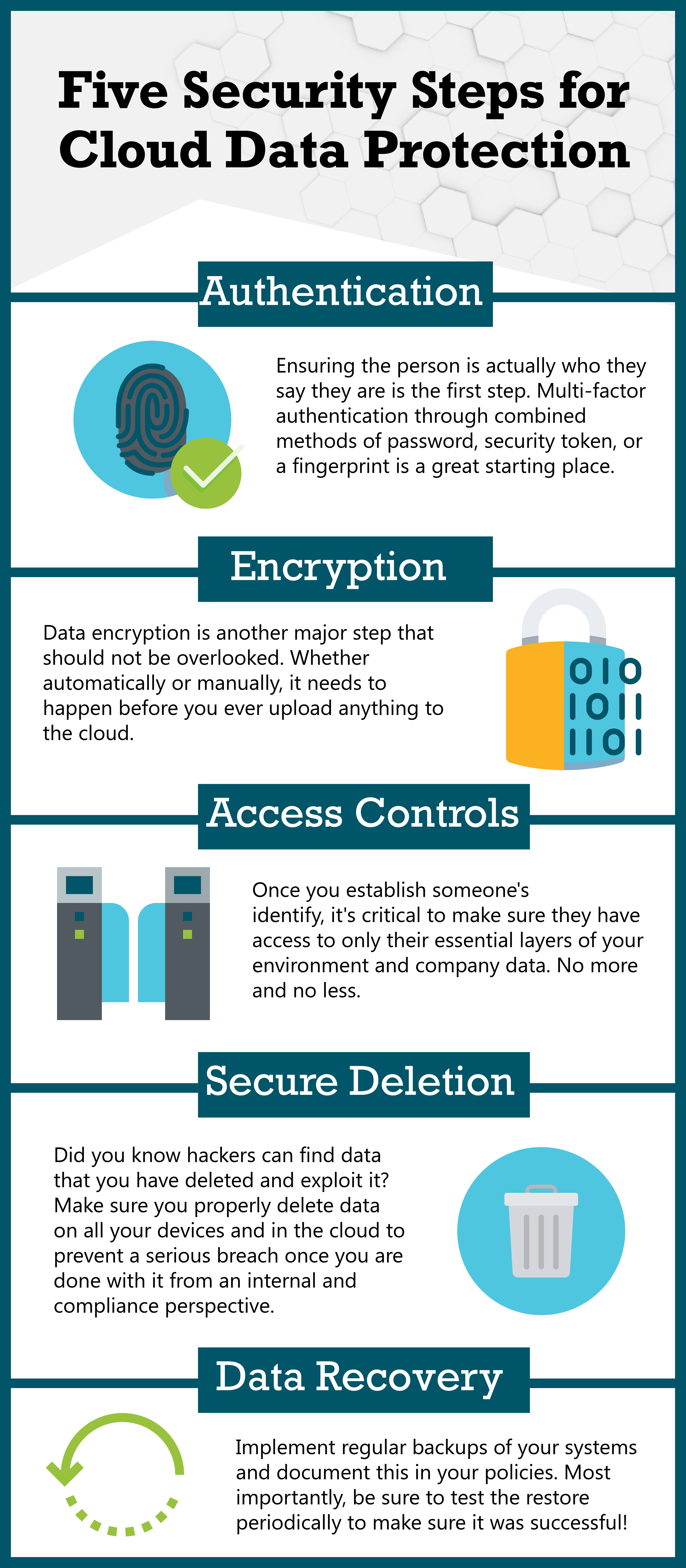
2. Data Encryption
Cloud security isn't just about who gets in but also about protecting data at rest and in transit:
- Data-at-Rest Encryption: Encrypt data stored in the cloud to ensure that unauthorized access will result in unusable data.
- Encryption in Transit: Use TLS (Transport Layer Security) or SSL (Secure Sockets Layer) to encrypt data as it moves between the user's device and the cloud provider.
- Key Management: Implement a robust key management system to control who has access to decryption keys.
Types of Encryption
| Encryption Type | Description |
|---|---|
| AES (Advanced Encryption Standard) | Commonly used for encrypting data at rest. Comes in several key sizes: 128, 192, or 256 bits. |
| RSA (Rivest-Shamir-Adleman) | Asymmetric encryption often used for securing data in transit and for key exchange. |
🔑 Note: Always use strong encryption algorithms and regularly rotate encryption keys to minimize security risks.
3. Network Security
Network-level security is crucial for protecting cloud environments from external and internal threats:
- Firewalls: Deploy next-generation firewalls that offer application-level filtering, intrusion prevention, and advanced malware protection.
- Network Segmentation: Divide your network into smaller, secure segments to contain breaches and prevent lateral movement by attackers.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): Use VPNs for secure remote access to cloud resources.
Enhancing Network Security Measures
- Employ intrusion detection/prevention systems (IDS/IPS) to identify and mitigate threats in real-time.
- Use Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) systems to monitor network activity and detect anomalies.
4. Continuous Monitoring and Logging
Cloud environments are dynamic, requiring constant vigilance:
- Log Analysis: Implement comprehensive logging to track user activity, system changes, and security events.
- Real-Time Alerts: Set up alerts to notify administrators of suspicious activities or policy violations.
- Audit Trails: Maintain detailed audit trails to investigate security incidents or compliance breaches.
Tools for Continuous Monitoring
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM) tools can automatically assess, manage, and enforce cloud security policies.
- Real-time anomaly detection systems help in identifying unauthorized or unusual behavior.
🚦 Note: Ensure that monitoring tools are integrated with your cloud provider's services for seamless operation.
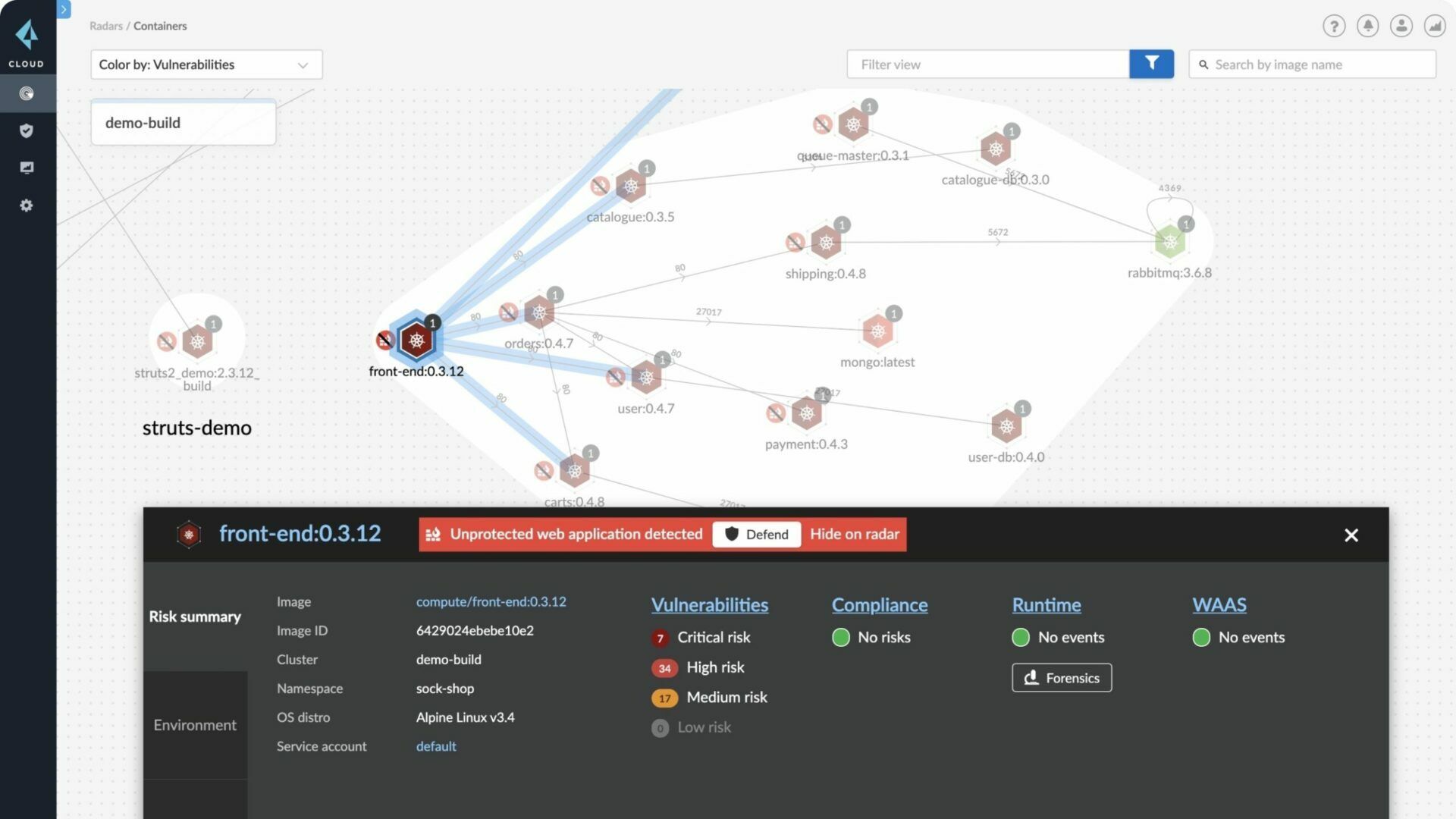
5. Incident Response and Disaster Recovery
Despite best efforts, security incidents can occur. Here's how to prepare:
- Develop an Incident Response Plan: Outline steps to detect, contain, eradicate, and recover from security incidents.
- Regular Testing: Perform simulated breach exercises to refine your response strategy.
- Disaster Recovery: Plan for disaster recovery to ensure business continuity, including data backup and recovery in different cloud regions.
Steps for an Effective Incident Response
- Document the incident details, including time, impact, and response actions.
- Contain the incident to prevent further damage or spread.
- Investigate the root cause to learn and prevent future occurrences.
Cloud computing offers unprecedented advantages, but it also introduces a new set of security concerns. By implementing these five essential tips—robust identity and access management, data encryption, network security, continuous monitoring, and a well-defined incident response and disaster recovery plan—organizations can significantly reduce their exposure to cyber risks. As cloud environments evolve, so too should the strategies to secure them. Constant vigilance, proactive measures, and staying informed about emerging threats are key to maintaining a secure cloud infrastructure.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
+
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is an authentication method that requires a user to provide two or more verification factors to gain access to a resource. These factors could include something you know (like a password), something you have (like a smartphone), or something you are (like a fingerprint).
How often should we conduct IAM access reviews?
+
IAM access reviews should be conducted at least quarterly, but it’s beneficial to do so after significant organizational changes like employee departures or role changes, to ensure access rights are still relevant and secure.
Why is network segmentation important for cloud security?
+
Network segmentation helps to limit the lateral movement of attackers in the event of a breach. By dividing your network into smaller, isolated segments, you can contain the impact of a security incident, making it harder for an attacker to compromise additional systems.
Related Terms:
- cloud security best practices 2019
- best practices for cloud security
- how to improve cloud security
- cloud security concerns best practices
- how to manage cloud security
- cloud security monitoring best practices