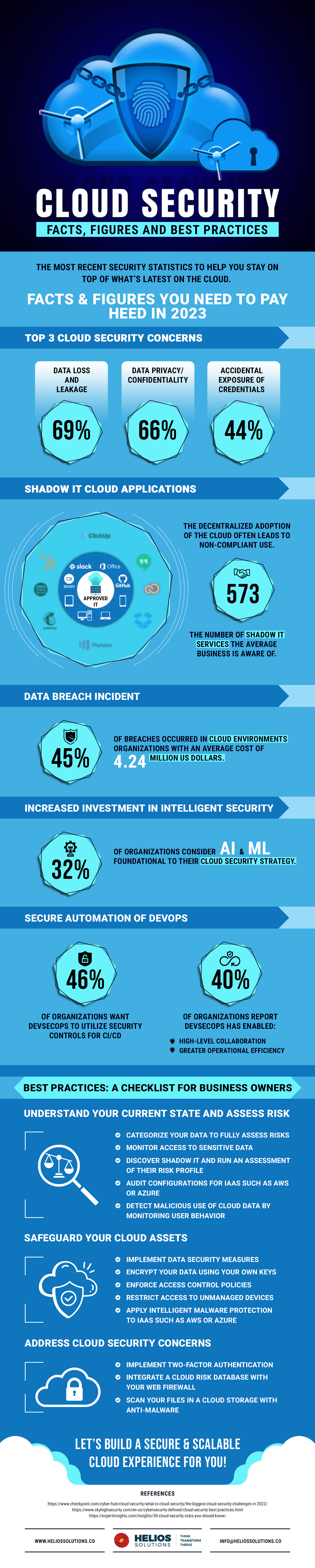
Protecting Your Data in the Cloud: Essential Security Tips

In an era where digital transformation is not just a buzzword but a reality in every aspect of our lives, moving data to the cloud has become almost second nature. Whether it's for personal backup or to run complex enterprise applications, the convenience of cloud computing is undeniable. However, with this convenience comes a critical responsibility — the protection of your data. This blog post will guide you through the essential security tips for safeguarding your data in the cloud.
Understanding Cloud Security

Cloud security encompasses several layers of protection, including:
- Data encryption
- Identity and access management (IAM)
- Regular updates and patches
- Network security
- Endpoint security
Essential Tips for Cloud Security
1. Choose a Reputable Cloud Service Provider
The foundation of secure cloud storage is selecting a provider with a solid track record in data protection. Look for:
- Compliance with international security standards
- Robust data center security
- Regular security audits and certifications
- Transparency in security practices and policies
2. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an extra layer of security by requiring more than one form of verification before granting access to cloud services. Here’s how you can implement it:
- Enable MFA for all user accounts
- Use authentication apps like Google Authenticator or Authy
- Consider biometric verification if available
3. Data Encryption
Encrypting your data ensures that even if someone gains unauthorized access, the data remains unreadable. Focus on:
- Encryption at rest and in transit
- Using strong encryption algorithms like AES-256
- Key management to control access to encryption keys
4. Regular Backups and Redundancy
Cloud storage should never be your only backup strategy:
- Schedule regular backups to offsite locations
- Employ data redundancy across multiple cloud regions
5. Access Control and Management
Controlling who can access your data is critical:

| Control Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) | Assigns permissions based on roles within your organization. |
| Time-Based Access Control | Restricts access to specific times or time frames. |
| Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) | Provides access based on a combination of user attributes, environmental conditions, and resource properties. |
6. Keep Software and Services Updated
Regular updates are crucial:
- Ensure automatic updates are enabled for all cloud services
- Patch vulnerabilities in your applications promptly
7. Use Security Groups and Network Firewalls
Utilize security groups and firewalls:
- Limit access to your cloud resources to specific IP addresses or ports
- Implement Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) for an extra layer of network isolation
8. Regular Security Audits and Monitoring
Constant vigilance is key:
- Conduct regular security audits
- Use cloud provider’s logging and monitoring tools to track suspicious activities
- Implement intrusion detection systems (IDS)
9. Secure API Access
APIs are the backbone of cloud services; securing them is paramount:
- Use API keys, OAuth tokens, and limit access to trusted sources
- Regularly review and audit API usage and access rights
10. Employee Training and Awareness
Education is often overlooked but is crucial:
- Provide training on security best practices
- Conduct phishing simulations to test employee awareness
Securing your data in the cloud involves a multifaceted approach, combining technology, policy, and human vigilance. While these tips cover a wide range of security measures, the dynamic nature of cloud technology means you must stay informed and proactive about emerging threats and evolving security practices.
How often should I update my cloud applications?
+It’s best to enable automatic updates for all cloud services to ensure you receive security patches as soon as they are available. Manual updates should be checked at least monthly.
What is the difference between encryption at rest and in transit?
+Encryption at rest secures data when it’s stored in the cloud. Encryption in transit protects data as it travels across the internet or between your local device and the cloud.
Can I trust any cloud provider with my sensitive data?
+Trust should be earned by providers through compliance with security standards, transparency in practices, and having robust security measures in place. Always do due diligence before choosing a provider.
How do I know if my cloud data has been compromised?
+Unusual activity, login attempts from unfamiliar locations or devices, unexpected password change notifications, and logs of failed access attempts are indicators. Regular monitoring and intrusion detection systems help in identifying breaches.
Related Terms:
- Data lifecycle policies
- Data lifecycle policy
- Principle of least privilege
- Data life cycle policy
- cloud data protection best practices
- data protection with cloud computing