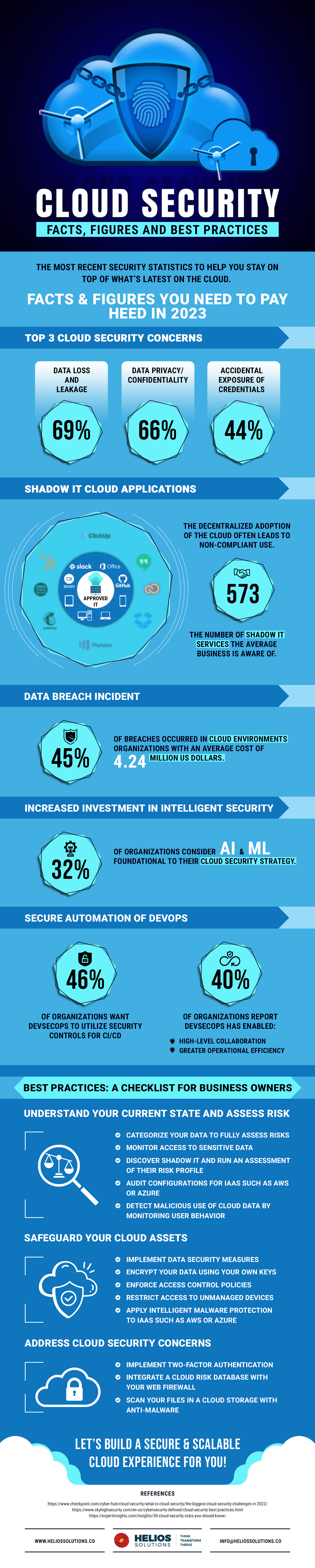
5 Essential Tips for Cloud Network Security

In today's digital world, where data breaches and cyberattacks have become commonplace, ensuring the security of your cloud networks is not just a luxury but an absolute necessity. Cloud computing offers numerous benefits, including scalability, flexibility, and cost-efficiency. However, these advantages come with the responsibility to safeguard your cloud infrastructure against various threats. Here are five essential tips to strengthen your cloud network security practices:
1. Implement Strong Access Control

Access control forms the bedrock of any secure environment, and cloud networks are no exception. Here are some ways to fortify your access control:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign permissions based on roles rather than individual identities to minimize the risk of over-privileged users.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to add an additional layer of security, ensuring that users must verify their identity in multiple ways before gaining access.
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Use IAM solutions to manage user identities and control their access to resources within your cloud environment.
2. Utilize Encryption Everywhere
Encryption is one of the most effective ways to protect data from unauthorized access:
- Encrypt Data at Rest: Use server-side encryption or client-side encryption to secure data that isn’t actively in use.
- Encrypt Data in Transit: Ensure that all data moving within or out of your cloud environment is encrypted via protocols like TLS/SSL.
- Key Management: Implement robust key management practices, keeping encryption keys secure and separate from the data itself.
🔒 Note: Ensure your encryption protocols are up-to-date, as outdated algorithms can become vulnerabilities.
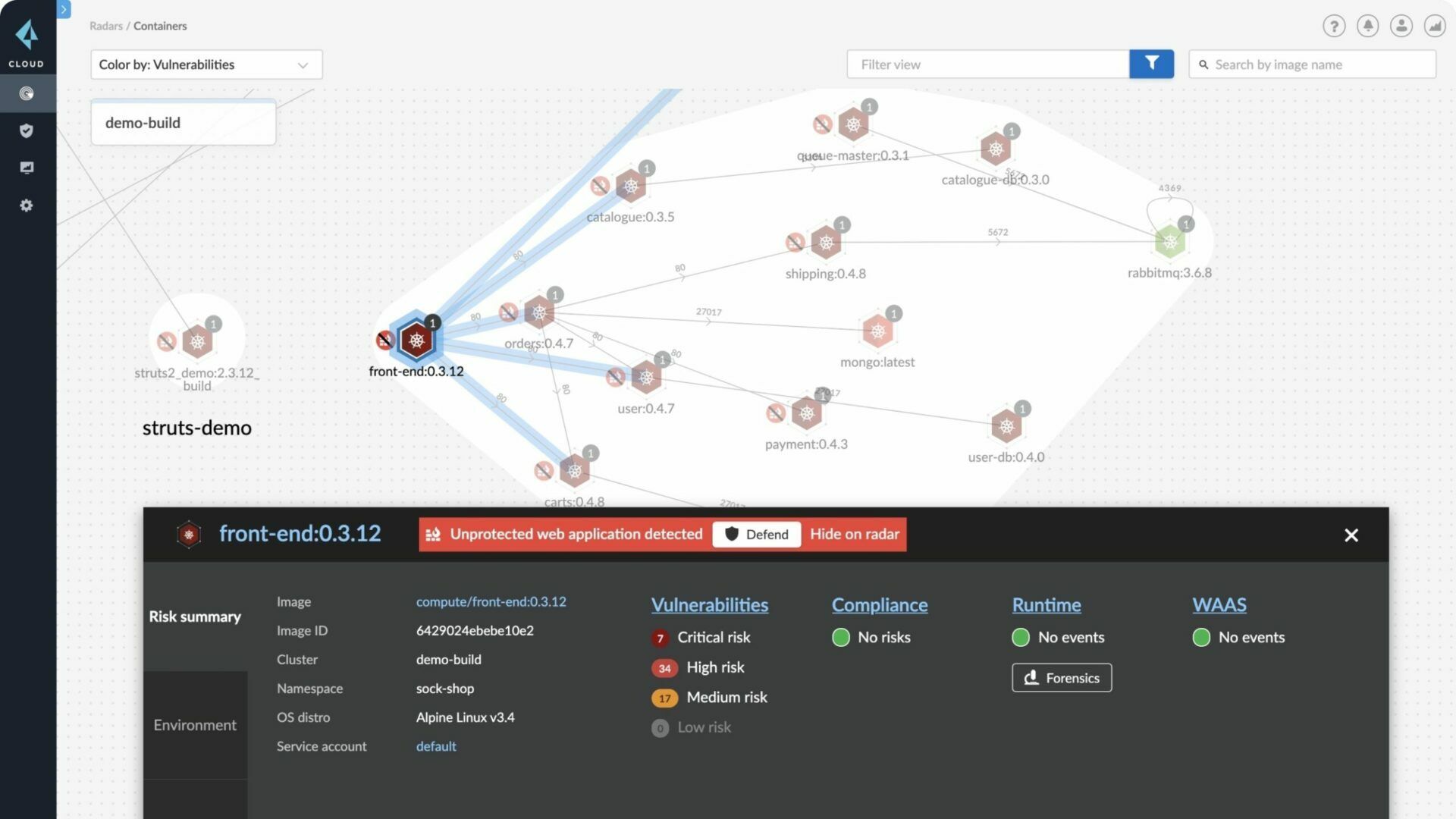
3. Regular Security Audits and Monitoring

Constant vigilance is key in cloud environments:
- Security Audits: Conduct regular audits to identify vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and compliance issues.
- Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS): Deploy IDS to monitor network traffic for suspicious activities.
- Logging and Monitoring: Utilize cloud-native tools to log activities, making it easier to track and investigate security incidents.
4. Leverage Advanced Threat Protection
Cloud platforms are prime targets for advanced cyber threats:
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB): Use CASB to enforce security policies, detect threats, and help maintain compliance.
- Network Security: Implement firewalls, network segmentation, and web application firewalls (WAF) to mitigate threats at the network level.
- AI and Machine Learning: Employ AI-driven solutions for predicting and automatically responding to cyber threats.
5. Develop a Comprehensive Incident Response Plan
Even with the best security practices, breaches can occur. Here’s how to prepare:
- Plan Development: Create a detailed incident response plan that outlines detection, response, and recovery steps.
- Regular Testing: Regularly test your incident response plan to ensure its effectiveness.
- Communication Strategy: Plan how you will communicate with customers, stakeholders, and authorities in the event of an incident.
In the rapidly evolving realm of cloud computing, safeguarding your cloud network infrastructure is paramount. By implementing strong access control, encryption, continuous monitoring, advanced threat protection, and a solid incident response plan, you can significantly reduce the risk of data breaches and maintain the trust of your clients and stakeholders. This comprehensive approach ensures that your cloud environment remains a secure, efficient platform for your business operations, fostering growth and innovation while mitigating security risks.
What is Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
+Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) is a security system that requires more than one method of verification to grant access to resources. This often includes something you know (like a password), something you have (like a smartphone or token), or something you are (like biometrics).
Why is encryption important for cloud security?
+Encryption is crucial for cloud security because it protects data at rest and in transit. By converting readable data into unreadable code, encryption ensures that even if data is compromised, it remains secure against unauthorized access.
How often should I perform security audits?
+It’s recommended to conduct security audits at least quarterly or after significant changes in your cloud environment. However, automated tools can continuously monitor security to reduce the gap between audits.
Related Terms:
- cloud security best practices 2019
- best practices for cloud security
- how to improve cloud security
- cloud security concerns best practices
- how to manage cloud security
- cloud security monitoring best practices