Cloud Computing Made Easy for Small Businesses

Cloud computing has rapidly become an integral part of modern business operations, particularly for small businesses that look to streamline their operations, save on costs, and scale their infrastructure with ease. This technology offers a myriad of benefits, from reduced IT expenses to enhanced flexibility and security. But what exactly is cloud computing, and how can small businesses leverage it effectively? Let's delve into the world of cloud computing to understand its applications for small enterprises.
What is Cloud Computing?
At its core, cloud computing involves delivering computing services over the internet. This model provides a range of on-demand resources like servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and more, without the need for substantial upfront capital investment in physical hardware. Here’s how it breaks down:
- On-Demand Self-Service: Businesses can provision and manage their computing resources as needed, without human interaction with a service provider.
- Broad Network Access: Resources are accessible over the internet from anywhere, at any time.
- Resource Pooling: The provider’s computing resources are pooled to serve multiple consumers using a multi-tenant model.
- Rapid Elasticity: Cloud services can quickly scale up or down to match demand.
- Measured Service: Resource usage can be monitored, controlled, and reported, providing transparency for both provider and customer.
Why Should Small Businesses Care?
For small businesses, the allure of cloud computing lies in its numerous advantages:
- Cost Reduction: Cloud solutions eliminate the need for significant hardware investments, reducing both initial capital expenditure and ongoing maintenance costs.
- Flexibility and Scalability: As your business grows or your needs change, cloud resources can be adjusted accordingly, ensuring you’re not overpaying for unused services.
- Disaster Recovery: Cloud-based backup solutions provide robust data protection, enabling businesses to recover quickly from data loss or disasters.
- Security: Cloud providers typically offer advanced security features, often exceeding what small businesses could afford or manage on their own.
- Mobility: Access your business applications and data from anywhere, enabling remote work and collaboration.
Types of Cloud Services
Cloud computing services are categorized into three main types:

| Type | Description | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) | Basic building blocks for cloud IT, providing access to fundamental resources like processing power, storage, and networks. | AWS EC2, Google Compute Engine |
| Platform as a Service (PaaS) | Platforms allowing customers to develop, run, and manage applications without complexity of building and maintaining the infrastructure typically associated with developing and launching an app. | Microsoft Azure, Heroku |
| Software as a Service (SaaS) | Delivery of software applications over the internet, managed by a third-party provider. This type of service is most widely used by businesses of all sizes. | Google Workspace, Salesforce |
Implementing Cloud Computing in Small Businesses
Here’s how small businesses can implement cloud computing:
- Assess Your Needs: Begin by understanding what aspects of your business would benefit from cloud migration. Is it data storage, application hosting, collaboration tools, or something else?
- Choose the Right Provider: Not all cloud services are created equal. Consider reliability, cost, security, scalability, and customer support when selecting a provider.
- Migration Strategy: Plan your migration carefully. Will you move everything at once, or take a phased approach? Understand your data, applications, and infrastructure before you proceed.
- Training: Ensure your staff is trained in the new systems. Cloud computing often changes how data and applications are managed.
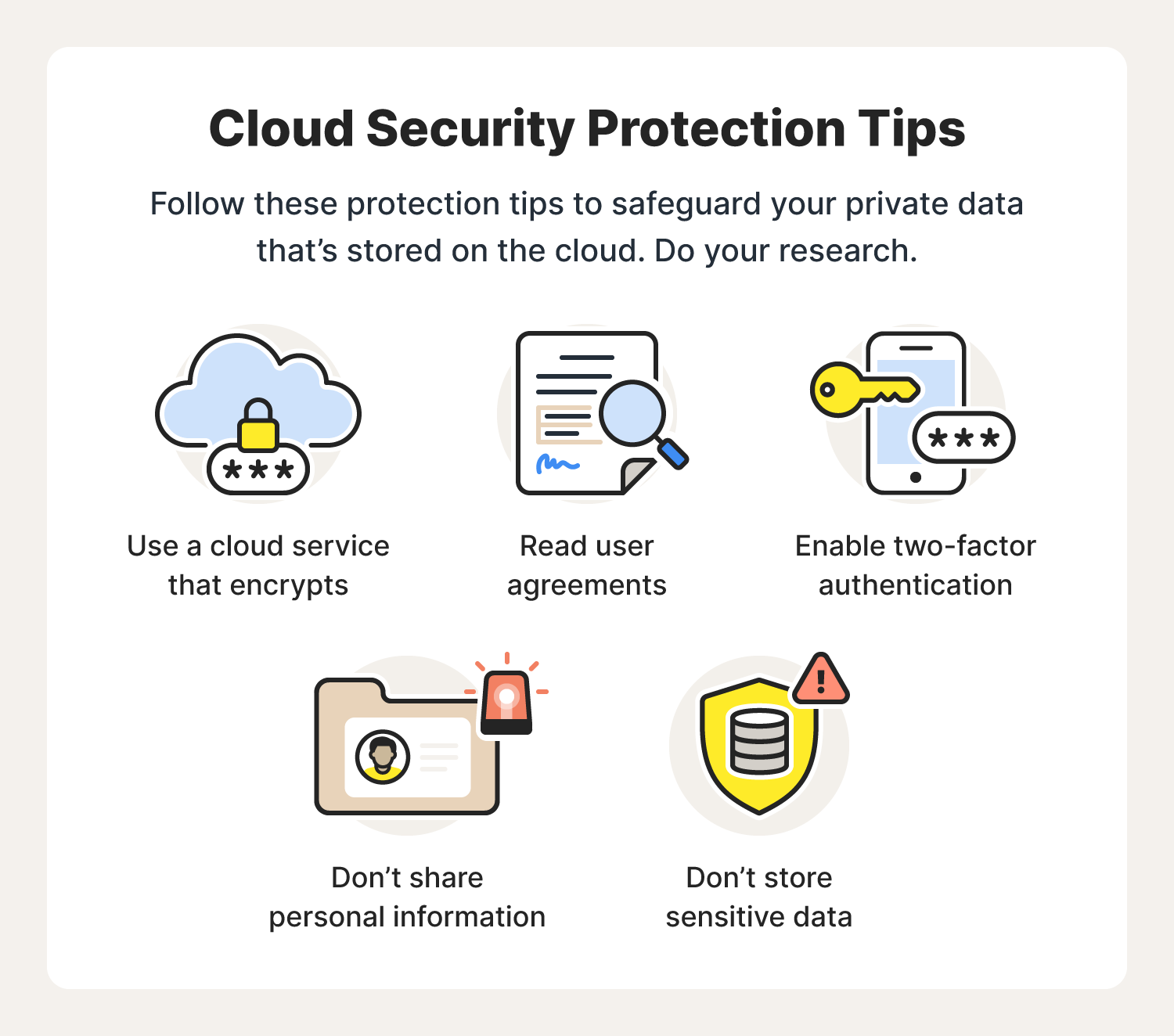
- Security Measures: Implement cloud security best practices like encryption, access controls, and regular audits.
- Continuous Improvement: Keep reviewing your cloud strategy. The cloud environment evolves rapidly, and your business should adapt to stay competitive.
The Financial Aspect
Cloud computing can significantly impact your financials:
- Operational Costs: Pay as you go model helps reduce operational expenses by only paying for what you use.
- Capital Expenditure: Shifting from CAPEX to OPEX allows for more flexible budgeting and reinvestment in other areas of the business.
- ROI: Cloud services can speed up your return on investment due to lower initial costs, quicker deployment, and the ability to scale according to demand.
💡 Note: Keep in mind that while cloud computing reduces initial capital outlays, ongoing costs can accumulate if not managed well.
Overcoming Challenges
While the benefits are clear, there are challenges to address:
- Compliance: Ensure your cloud provider adheres to necessary industry and regulatory compliance standards.
- Data Security: Despite the security offered by cloud providers, additional measures are often required to secure sensitive data.
- Integration: Integrating existing systems with cloud services can be complex, requiring careful planning.
- Dependency on Internet: Cloud computing depends on internet connectivity. Ensure your business has reliable access.
🔧 Note: Consider hybrid solutions that blend on-premises infrastructure with cloud services to mitigate some of these risks.
Recapitulation
To wrap up, cloud computing offers small businesses a robust platform to grow efficiently and cost-effectively. It facilitates scalability, cost savings, mobility, and advanced security measures. By assessing needs, choosing the right provider, carefully planning migration, and maintaining a continuous improvement mindset, small businesses can leverage the cloud to their advantage. This technological shift not only reduces the burden of IT management but also enables businesses to focus on their core competencies, ultimately fostering growth and innovation.
Is cloud computing secure for small businesses?
+Yes, cloud computing can be very secure for small businesses. Cloud providers invest heavily in security measures that often exceed what many small businesses can afford on their own. However, businesses must take responsibility for securing their own data with encryption, strong password policies, and regular security audits.
How can cloud computing help with business continuity?
+Cloud computing aids in business continuity by offering disaster recovery and data backup solutions. In the event of a disaster, cloud services can quickly restore data and applications, minimizing downtime.
What’s the cost of moving to the cloud for small businesses?
+The initial cost can be low as it eliminates the need for purchasing hardware. However, ongoing costs depend on usage. Businesses might incur expenses for data transfer, storage, compute resources, and additional services. Proper planning and cost management are crucial to keep expenses in check.
Can a small business move all its operations to the cloud?
+Yes, but it requires careful planning. Some businesses might find a hybrid approach more suitable, where sensitive or legacy systems remain on-premises while leveraging the cloud for scalability and flexibility.
What training is required for staff to use cloud services?
+Staff need to be trained on the cloud platform they’re using, understanding concepts like data management, security practices, and application deployment. Most cloud providers offer resources and training programs to get staff up to speed.
Related Terms:
- Cloud server for small business
- Rise of cloud computing
- Cloud Business
- Cloud computing disadvantages
- Cloud computing statistics
- Cloud computing report