5 Essential Tips for Securing Cloud Computing

The rise of cloud computing has transformed how businesses manage, store, and access data. While the benefits are manifold, including scalability, cost efficiency, and accessibility, there's also an increased responsibility to ensure cloud security. Here, we'll explore five essential tips to secure your cloud computing environment, ensuring both your business operations and data remain safe.
1. Understand Your Cloud Provider’s Security Responsibilities
Before diving into specific security measures, it’s crucial to understand what your cloud service provider (CSP) is responsible for and where your responsibilities begin:
- Shared Responsibility Model: Cloud providers usually secure the infrastructure, while customers secure their data, applications, and configurations.
- Service Level Agreements (SLAs): Review these to understand the security measures, compliance certifications, and the provider’s commitment to security.
- Data Encryption: Most CSPs encrypt data at rest and in transit, but ensuring your data’s encryption keys are managed correctly is your responsibility.
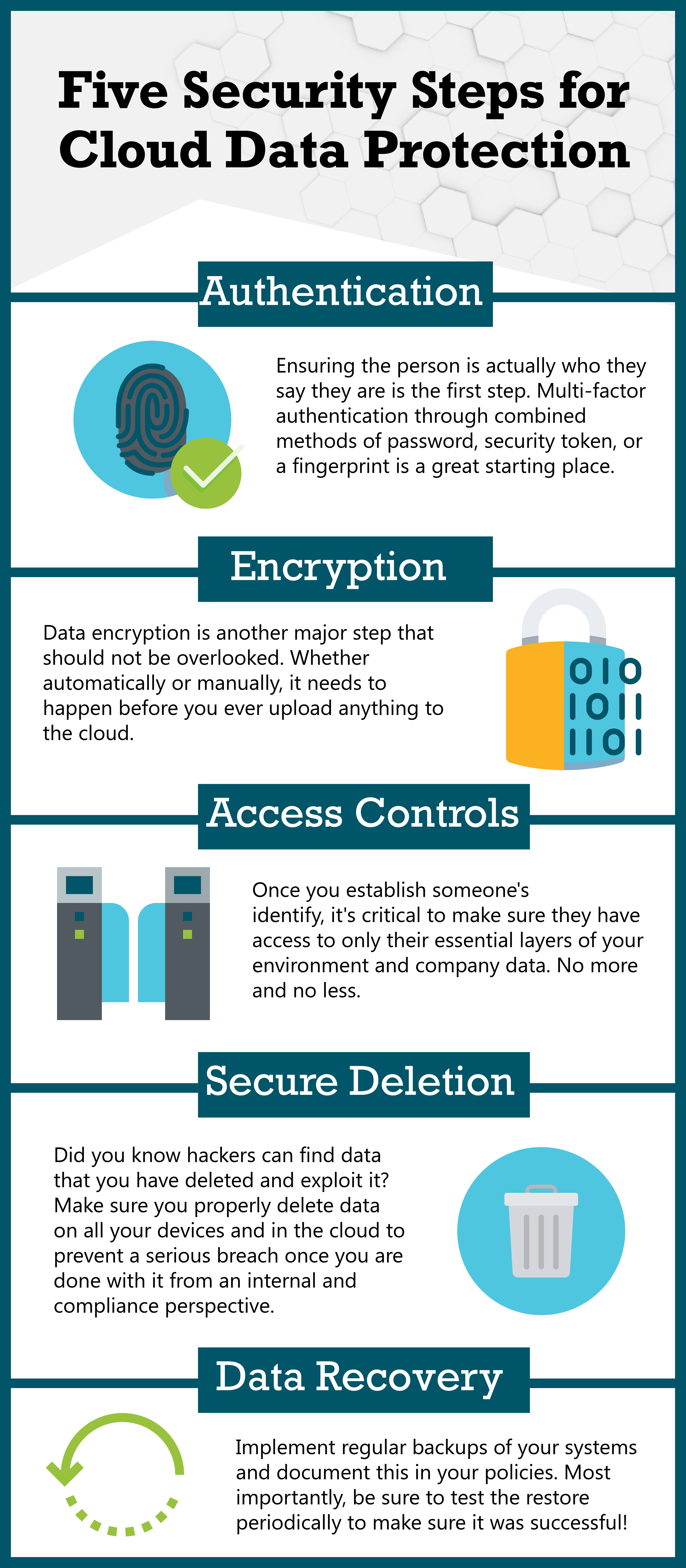
2. Implement Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management is pivotal in controlling who can do what within your cloud environment. Here are key steps:
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign roles with least privilege to minimize risks.
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enforce MFA for all users, especially for access to sensitive data.
- Regular Audits: Audit user permissions regularly to remove or adjust unnecessary access.
- Centralized Logging: Implement logging to track access and changes in permissions.
3. Keep Your Systems and Applications Updated
Security patches and updates are your first line of defense:
- Automated Updates: Enable automated patching for your operating systems, applications, and cloud services.
- Proactive Monitoring: Use monitoring tools to identify and patch vulnerabilities swiftly.
- Third-Party Software: Ensure any third-party applications are kept up-to-date, as they can be a source of vulnerabilities.
4. Secure Data with Encryption and Backup Strategies
Data security involves protecting data both when it’s in transit and at rest:
- Encryption in Transit: Use protocols like TLS to encrypt data as it moves between your cloud environment and users or between cloud services.
- Encryption at Rest: Ensure data is encrypted when stored in the cloud using strong encryption standards.
- Backups: Implement a robust backup strategy to recover from data loss or breaches.
⚠️ Note: Regularly test your backups to ensure they can be restored when needed.
5. Regular Security Assessments and Compliance
Security is not a one-time setup; it’s an ongoing process:
- Vulnerability Scanning: Conduct regular scans to identify potential vulnerabilities.
- Penetration Testing: Simulate cyber-attacks to uncover weaknesses before real threats do.
- Compliance Checks: Ensure your cloud environment complies with industry standards like GDPR, HIPAA, or ISO 27001.
In this final paragraph, we've reviewed the key strategies for securing cloud computing. From understanding your CSP's role to maintaining strict access controls, regularly updating systems, securing data with encryption, and conducting ongoing security assessments, these steps form a comprehensive security plan. Implementing these tips ensures not only compliance with regulations but also the protection of your business against the evolving threats in the cloud landscape.
What is the Shared Responsibility Model in Cloud Security?
+In cloud computing, the Shared Responsibility Model dictates that the cloud provider is responsible for security of the cloud infrastructure, including the hardware, software, and network environment. Meanwhile, the customer is responsible for securing their applications, data, operating systems, network traffic, access management, and user account security.
How often should security assessments be conducted in the cloud?
+Security assessments should be conducted at least quarterly or whenever there are significant changes to the cloud environment, such as system upgrades, new deployments, or changes in configurations. However, for high-risk environments or sensitive data, more frequent assessments might be necessary.
Can I trust my cloud provider with data encryption?
+Most cloud service providers offer encryption for data at rest and in transit. However, it’s crucial to manage encryption keys carefully. While CSPs provide encryption, customers must ensure they have control over the keys or use a key management service that integrates well with their security strategy.
Related Terms:
- what are cloud security types
- why we need cloud security
- different types of cloud security
- security measures in cloud computing
- how to secure your cloud
- cloud security monitoring best practices