Cloud Computing: Unlocking Data Security for Your Business
In the dynamic landscape of modern business, the shift towards cloud computing has been nothing short of revolutionary. Companies are increasingly embracing cloud technologies to streamline operations, reduce costs, and enhance flexibility. Yet, one of the most critical aspects that businesses are concerned about when transitioning to the cloud is data security. Today, let's dive into how cloud computing unlocks unparalleled levels of data security for your business.
Why Cloud Computing Enhances Data Security
Cloud computing involves the delivery of a range of computing services—servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence—over the internet. Here’s how it enhances security:
- Centralized Data Management: With cloud storage, data is housed in a centralized location, making it easier to manage and protect through advanced security measures like encryption.
- Advanced Security Protocols: Cloud service providers invest heavily in robust security measures, often surpassing what many businesses can afford on their own.
- Scalability: As your business grows, cloud services can scale their security measures to meet your needs without requiring significant investment in hardware.
- Redundancy: Cloud providers typically have multiple redundancies for data storage, reducing the risk of data loss due to hardware failure.
- Continuous Monitoring: Many cloud services include real-time monitoring and automatic updates, keeping security protocols at the forefront of defense against threats.
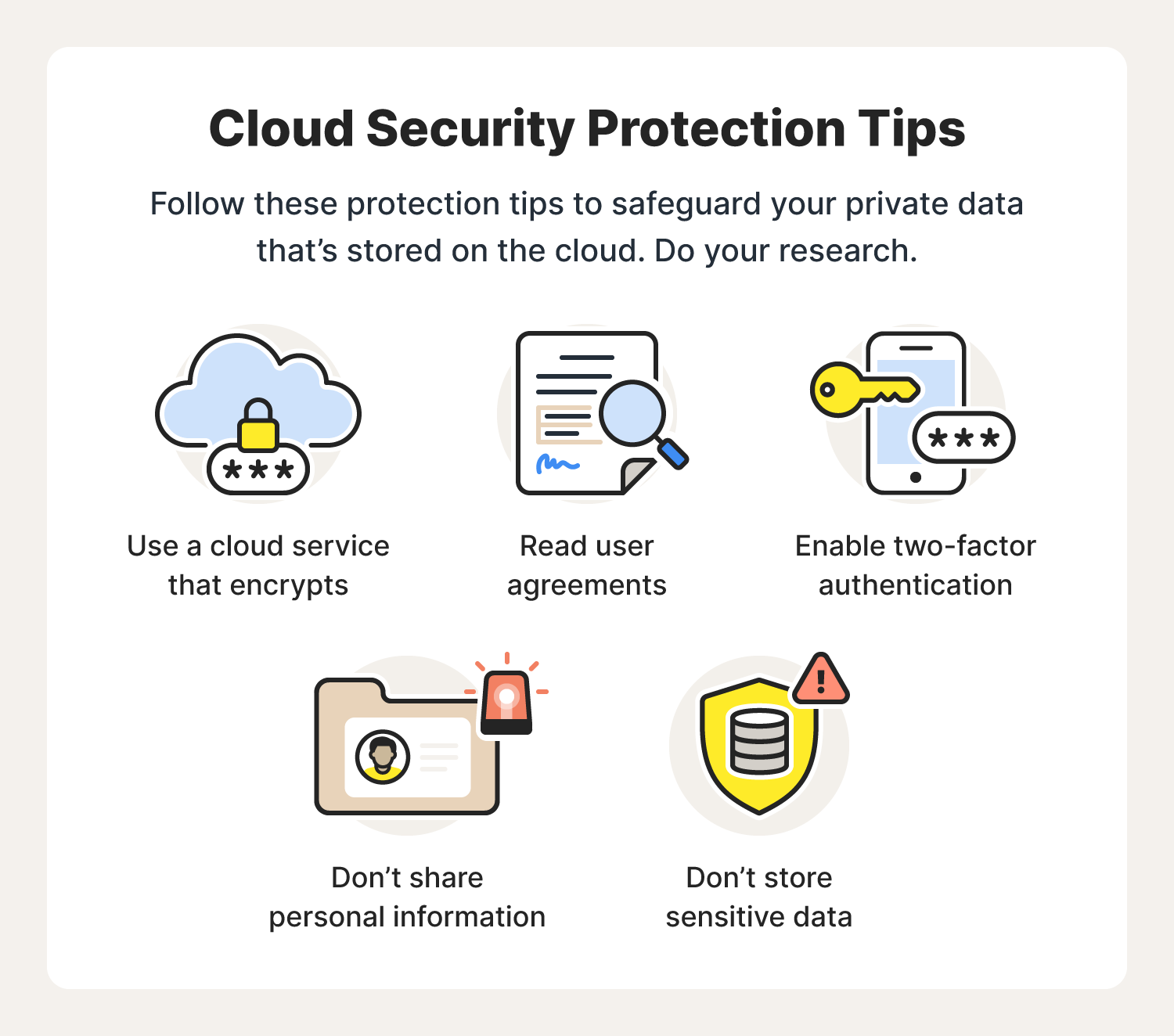
Encryption in the Cloud
Encryption is at the heart of cloud security:
- Data Encryption: Encrypting data both at rest and in transit ensures that if data is intercepted or accessed without authorization, it remains unreadable.
- Key Management: Providers often offer key management services, allowing businesses to maintain control over their encryption keys, thereby enhancing security without additional overhead.
- Zero-knowledge Encryption: Some services provide zero-knowledge privacy, where the provider itself has no access to the data or the encryption keys.
🔒 Note: Always verify the encryption standards your cloud provider uses and understand how they manage encryption keys to ensure that your data’s security aligns with your company’s compliance requirements.
Access Control and Identity Management
Controlling who can access your data is fundamental to cloud security:
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds layers of security, requiring more than one proof of identity before granting access.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Businesses can assign roles to employees, limiting access to only what is necessary for their job functions.
- Identity Governance: Cloud providers often include tools for automated governance to ensure compliance with various regulations regarding data access.
Compliance and Auditability
Cloud environments are designed with compliance in mind:
- Compliance Certifications: Providers often strive to meet industry standards like ISO 27001, HIPAA, PCI DSS, etc., ensuring that your data security practices meet legal and regulatory requirements.
- Auditing and Reporting: Cloud services offer detailed logging and reporting capabilities, which are crucial for audits and for maintaining compliance.
Protecting Against Threats
Cloud providers are equipped to tackle modern cyber threats:
- Threat Detection: Advanced systems detect anomalies and suspicious behavior, often using AI and machine learning to predict and prevent attacks.
- Incident Response: Automated response mechanisms can mitigate the impact of security breaches, minimizing damage.
- Distributed Denial of Service (DDoS) Mitigation: Cloud infrastructures often come with built-in DDoS protection, shielding your online services from overload attempts.
Disaster Recovery and Data Backup
Cloud computing can transform how you approach disaster recovery and data backup:
- Automated Backup: Regular, automatic backups are standard, reducing the risk of data loss due to human error or natural disasters.
- Geographic Redundancy: Data is often replicated in different geographic locations, ensuring availability in case of regional outages or disasters.
- Recovery Services: Many cloud providers offer disaster recovery as a service, which speeds up the process of restoring data and services post-disaster.
As businesses adopt cloud computing, they not only unlock scalability and cost efficiencies but also robust, enterprise-level security that might be challenging to replicate on-premises. The cloud can provide a secure environment through:
- Economy of scale in security investment
- Continuous updates and monitoring
- Compliance-focused environments
However, the responsibility for cloud security isn’t solely on the provider. Businesses must take active steps to ensure their data is secure by:
- Selecting a reputable cloud service provider
- Implementing strong internal security policies
- Ensuring compliance with industry-specific regulations
- Regularly reviewing and updating security practices
What makes cloud computing secure for data?
+Cloud computing is secure due to advanced encryption protocols, centralized management of security resources, and continuous monitoring for threats. Providers invest heavily in security infrastructure and practices, offering layers of protection that are often more comprehensive than what individual businesses might achieve on their own.
How do cloud services handle data encryption?
+Cloud services encrypt data both at rest (when stored) and in transit (during transmission). They use various encryption methods, often allowing customers to manage their own keys, providing additional security through zero-knowledge privacy where even the provider cannot access the data.
Can cloud computing help with regulatory compliance?
+Yes, cloud computing can help businesses meet compliance requirements through certified infrastructure, robust access controls, and detailed logging and reporting capabilities, which facilitate audits and maintain compliance with regulations like HIPAA, GDPR, and others.
Related Terms:
- security in cloud computing
- cloud data security solutions
- microsoft cloud data security
- cloud based data security
- cloud data security tools
- cloud based security