7 Essential Tips for Cloud Security
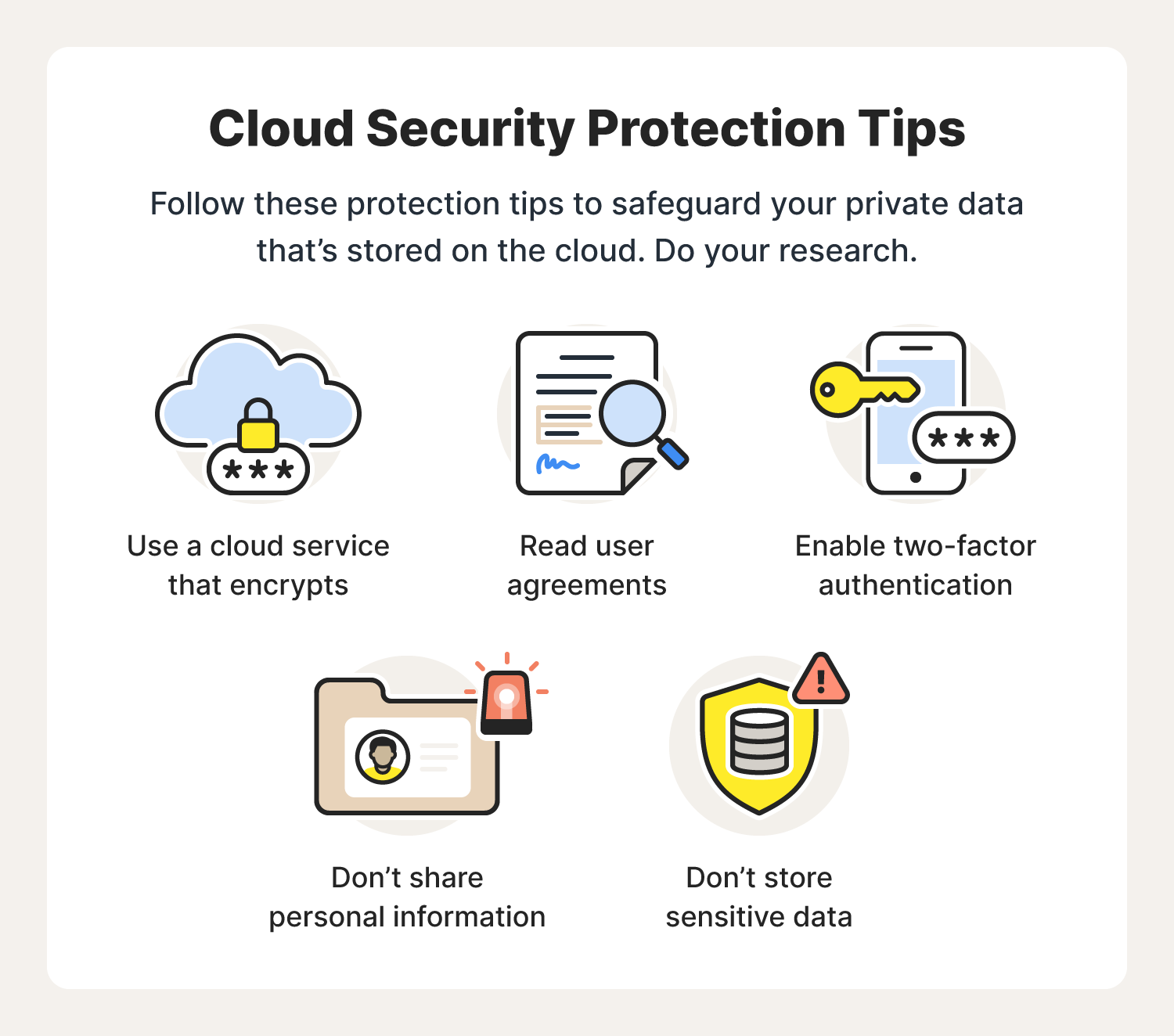
Cloud computing has transformed how businesses operate by providing scalable, flexible, and cost-effective solutions for storing, processing, and managing data. However, this shift to the cloud also brings with it a unique set of security challenges. Ensuring the safety of your data, applications, and infrastructure in the cloud is paramount. Here are seven essential tips for enhancing cloud security:
1. Implement Strong Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management (IAM) forms the backbone of cloud security. It ensures that the right individuals have the appropriate access to resources:
- Use Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Enable MFA to add an extra layer of security, making it much harder for unauthorized users to access your cloud resources.
- Principle of Least Privilege: Assign permissions strictly based on what users need to perform their job functions, reducing the risk of accidental or malicious misuse.
- Regularly Audit Access: Keep track of who has access to what and regularly review and adjust these permissions.
2. Encrypt Data at All Levels
Encryption is your first line of defense against data breaches:
- Data in Transit: Use Transport Layer Security (TLS) to secure data during transfer.
- Data at Rest: Implement encryption for data stored in cloud storage services to protect it even if the storage system is compromised.
- Key Management: Manage encryption keys with secure key management systems, keeping them separate from the data they protect.
3. Leverage Cloud Security Tools
Most cloud service providers offer robust security features:
- Security Groups: Configure these to limit access to your cloud services by defining which IP addresses or protocols can interact with your resources.
- Web Application Firewalls (WAF): Use WAFs to filter and monitor HTTP traffic to and from your web applications, blocking common attack vectors.
- Cloud Security Posture Management (CSPM): Deploy tools that continuously monitor cloud infrastructure for misconfigurations, compliance, and threats.
🔐 Note: Always stay updated with the security features your cloud provider offers, as they frequently update and enhance their security capabilities.
4. Regularly Update and Patch Systems
Keeping your cloud environment up-to-date:
- Automate Patching: Use automated tools to patch systems immediately when new vulnerabilities are discovered.
- Monitor for Unapproved Software: Ensure no unapproved software runs in your cloud environment, which could introduce vulnerabilities.
- Maintain an Inventory: Know what software is in use to facilitate quick patching when necessary.
5. Continuous Monitoring and Logging
Monitoring is key to identifying and responding to security incidents quickly:
- Real-time Monitoring: Implement tools that provide real-time insights into your cloud environment’s health and security status.
- Log Analysis: Regularly analyze logs to detect anomalies or unusual patterns that could indicate a security breach.
- Set Up Alerts: Configure alerts for critical events or suspicious activities to respond promptly.
6. Implement Network Security Measures
Securing your cloud network:
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): Use VPC to isolate your resources and control network traffic.
- Network Segmentation: Divide your network into segments to limit lateral movement within your cloud environment in case of a breach.
- Network Access Control Lists (NACLs): Configure NACLs to act as an additional layer of network protection.
7. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
Preparing for the worst:
- Regular Backups: Ensure data is regularly backed up to avoid data loss in case of a breach or system failure.
- Geographical Redundancy: Use multi-region deployments to keep your data available even during regional outages or disasters.
- Automated Failover: Set up systems that automatically shift workload to another region if a problem arises.
By adhering to these essential tips, you can significantly bolster your cloud security posture. Remember, cloud security is an ongoing process, not a one-time setup. Constant vigilance, regular audits, and staying informed about the latest threats are vital. With robust security measures in place, your business can leverage the cloud's full potential while keeping your data safe and secure.
What is the role of encryption in cloud security?
+
Encryption plays a crucial role in cloud security by protecting data both in transit and at rest. It ensures that even if data is intercepted or accessed without authorization, it remains unreadable without the correct decryption keys, thereby maintaining the confidentiality and integrity of your information.
Why is regular auditing of user permissions important?
+
Regular auditing of user permissions ensures that access rights are aligned with current roles and responsibilities within the organization. Over time, as roles change, permissions might become outdated or overly permissive, increasing the risk of insider threats or accidental data exposure. Auditing helps maintain the principle of least privilege and reduces potential vulnerabilities.
How can I ensure my cloud environment is always up to date with security patches?
+
To ensure your cloud environment stays current with security patches, automate the patching process. Use tools provided by your cloud service provider or third-party solutions that can automatically apply patches or notify you of available updates. Additionally, maintaining a software inventory and monitoring for unapproved software can help in efficient patching management.
Related Terms:
- Cloud security Fundamentals PDF
- Cloud security services
- Security challenges in cloud computing
- Securing cloud
- Cloud computing security controls
- Cloud security framework and architecture