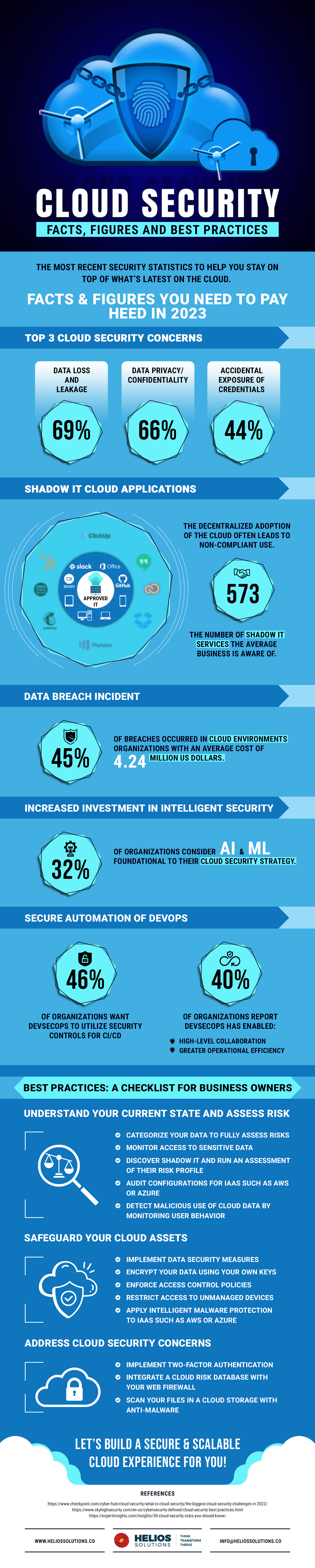
5 Essential Security Tips for Cloud Computing in 2023
Cloud computing has transformed the way businesses and individuals handle data, software, and applications. As organizations increasingly adopt cloud solutions, security has become a primary concern. In 2023, the dynamic nature of cloud environments and evolving cyber threats mean that robust security practices are more critical than ever. Here are five essential security tips to ensure your cloud computing environment remains secure:
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Identity and Access Management is the cornerstone of cloud security. It involves managing identities, authentication, and authorization in a way that ensures only the right people have access to the right resources.
- Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to provide two or more verification factors, reducing the risk of unauthorized access due to compromised credentials.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Assign roles to users based on their job function. This limits access to only the resources necessary for their role, minimizing insider threats.
- Regularly Review Access Permissions: Periodically review who has access to what within your cloud services to ensure permissions are still necessary and in line with current job functions.
- Use Identity Federation: Federated identity allows users to authenticate with one set of credentials across multiple systems, simplifying management while enhancing security through unified identity control.
🔐 Note: Continuous monitoring and updating of IAM policies help to prevent unauthorized access and ensure compliance with changing regulations.
2. Data Encryption
Data encryption is vital to protect the confidentiality and integrity of data both at rest and in transit.
- Encrypt Data at Rest: Use encryption for data stored in databases, file systems, or storage services. This ensures that even if data is accessed, it remains unreadable without proper decryption keys.
- Secure Data in Transit: Implement Transport Layer Security (TLS) or other encryption protocols for data transmission over networks. This prevents data interception by malicious actors.
- Key Management: Manage encryption keys securely. Cloud services often provide key management services (KMS), but internal best practices are crucial for key rotation, revocation, and storage.
🔑 Note: Strong encryption not only protects data but also ensures compliance with standards like GDPR or HIPAA, where data protection is a legal requirement.
3. Regular Security Assessments
The cloud environment changes frequently, and so do potential vulnerabilities. Regular security assessments are key to staying ahead of threats.
- Conduct Vulnerability Scans: Use automated tools to scan your cloud infrastructure for known vulnerabilities. Fix any issues identified promptly.
- Penetration Testing: Simulate attacks to test your security posture. External and internal penetration tests can reveal weaknesses in your cloud security.
- Compliance Checks: Ensure your cloud environment meets regulatory requirements through automated compliance scans and reporting.
- Audit Trails: Maintain detailed logs of all activities for forensic analysis in case of a security breach.
🔍 Note: Regular assessments help in adapting security measures to an ever-evolving cloud landscape, keeping your defenses robust and current.
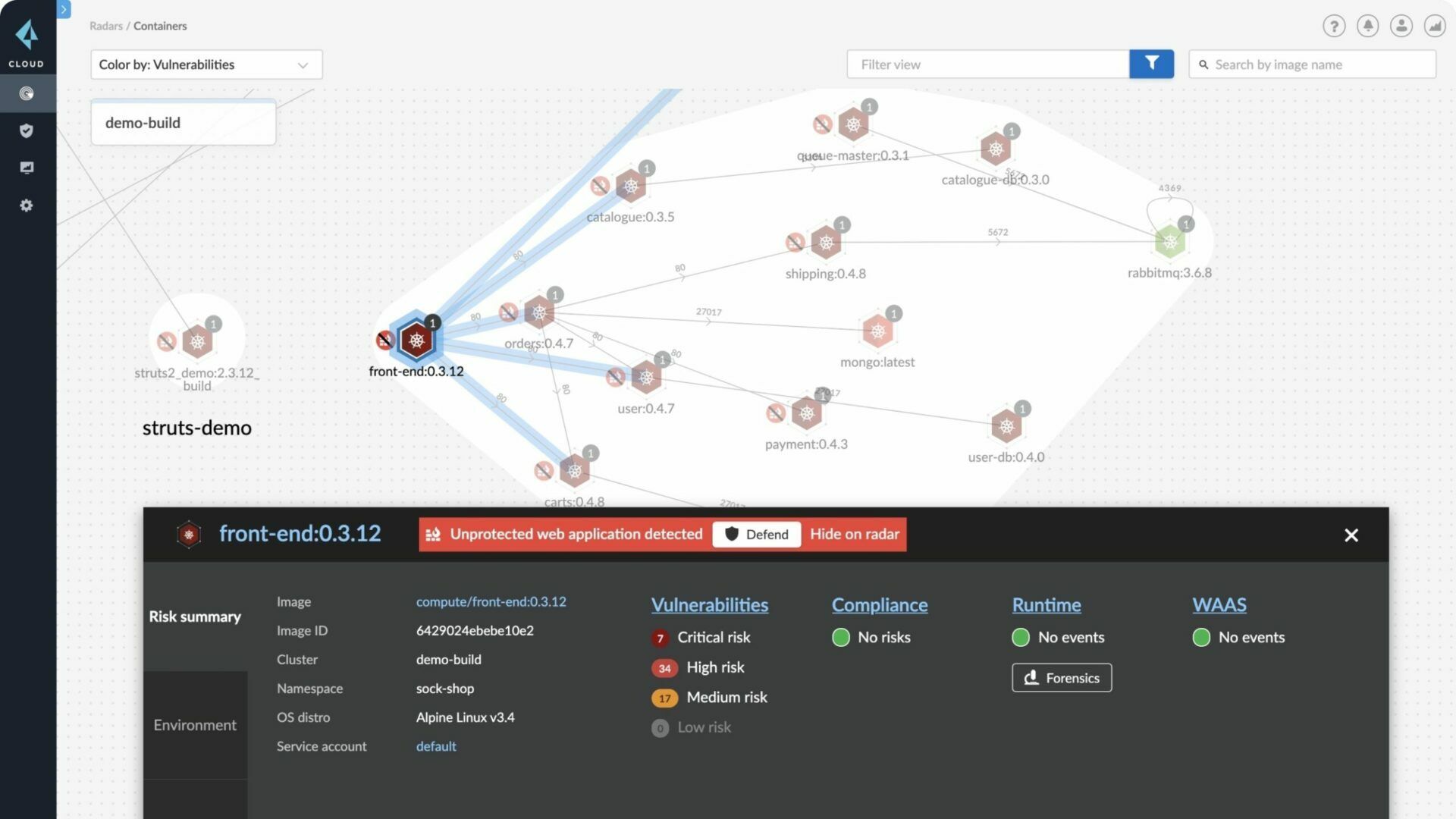
4. Network Security
Network security measures in the cloud are crucial to protect against unauthorized access, data breaches, and other cyber threats.
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): Utilize VPCs to isolate your cloud resources, creating a virtual network that connects your cloud resources securely.
- Security Groups and Network Access Control Lists (NACLs): Configure these to control inbound and outbound traffic to and from your resources, acting as virtual firewalls.
- Implement WAF (Web Application Firewall): Protect web applications by filtering and monitoring HTTP traffic to block malicious attempts.
- DDoS Protection: Use cloud services with built-in Distributed Denial of Service protection to mitigate volume-based attacks.
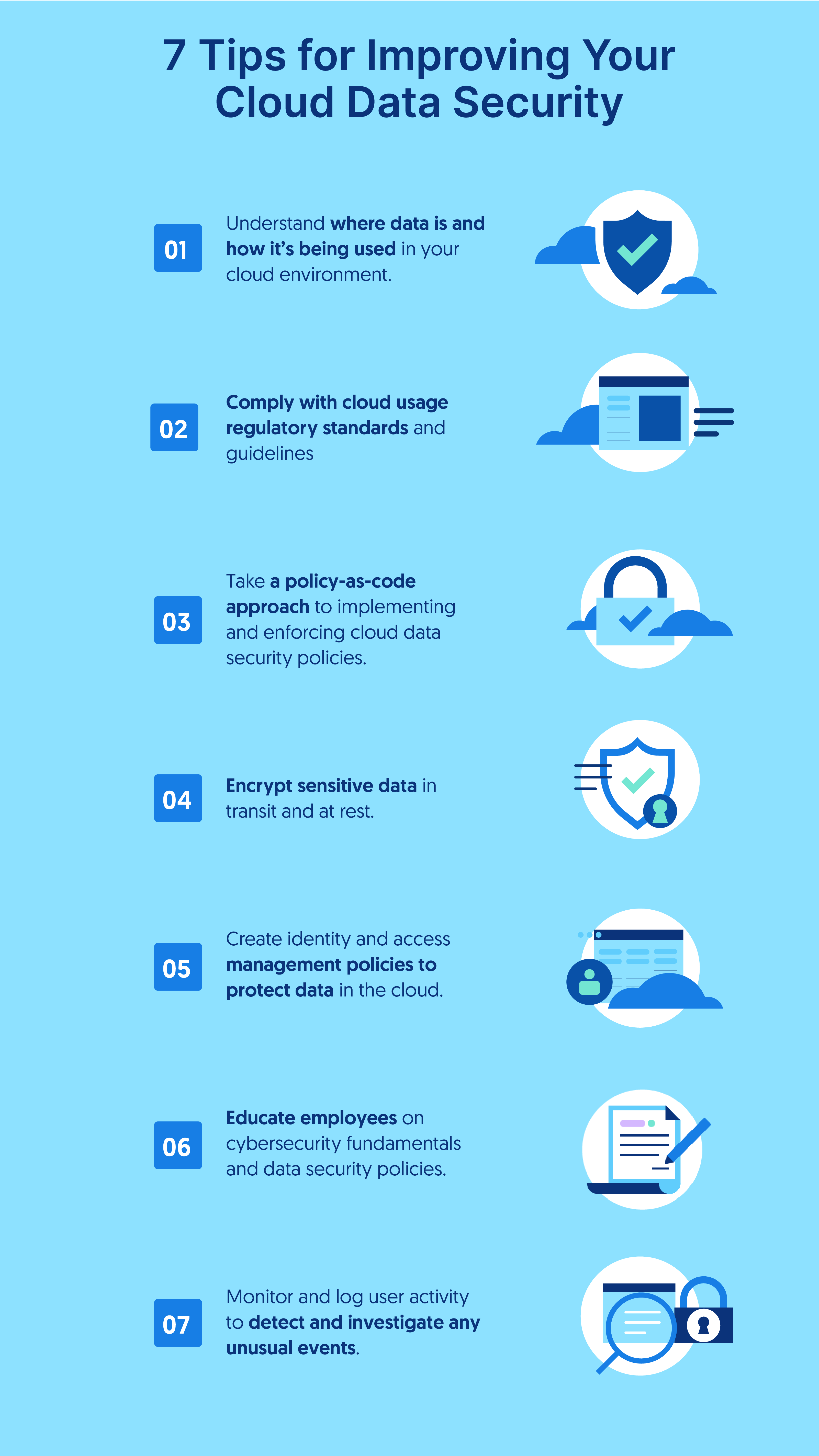
| Security Measure | Description |
|---|---|
| VPC | Creates a secure, isolated virtual network environment. |
| Security Groups | Acts as firewall rules at the instance level. |
| NACLs | Provides network traffic control at the subnet level. |
| WAF | Monitors, filters, and blocks web traffic to protect web applications. |
| DDoS Protection | Guards against Distributed Denial of Service attacks. |
🌐 Note: Effective network security configuration in the cloud ensures that your data and applications are safe from external threats.
5. Monitor and Respond
Proactive monitoring and swift response to security events are vital for cloud security management.
- Real-Time Monitoring: Implement real-time monitoring for anomalies, unauthorized access, or suspicious activities across your cloud infrastructure.
- Incident Response Plan: Have a clear incident response strategy in place. This should include detection, analysis, containment, eradication, and recovery phases.
- Automate Security Response: Use automated tools to respond to security events, like blocking IPs or adjusting access rights.
- Continuously Learn and Adapt: Learn from past security events or audits to continually improve your security protocols and procedures.
👀 Note: An effective security monitoring system not only detects issues but also enables a swift response, potentially reducing the impact of security incidents.
The adoption of cloud computing presents both opportunities and challenges in terms of security. By implementing strong IAM practices, ensuring data encryption, conducting regular security assessments, bolstering network security, and actively monitoring for and responding to security events, organizations can create a robust cloud security framework. These measures help in protecting valuable data, ensuring service continuity, and maintaining trust with customers and stakeholders. Remember, cloud security is an ongoing process; staying informed and adapting to new threats and technologies is essential for safeguarding your cloud environment in 2023 and beyond.
What are the benefits of using IAM in cloud computing?
+
Identity and Access Management (IAM) in cloud computing helps in controlling access to cloud resources, reducing security risks, and ensuring compliance. It simplifies user management, enforces least privilege access, and provides accountability through detailed audit logs.
How often should security assessments be conducted in the cloud?
+
Security assessments should be conducted at least quarterly or after significant changes to the cloud environment. For high-risk or highly regulated environments, monthly or even continuous assessments might be necessary.
Is cloud encryption necessary if my on-premises data is already encrypted?
+
Yes, encryption should be applied at both on-premises and cloud levels. Cloud encryption protects data during transit and at rest, safeguarding against unauthorized access even within the cloud provider’s infrastructure.