Cloud Computing: Enhancing Security Measures for Better Protection

Cloud computing has revolutionized the way businesses operate, enabling them to scale resources dynamically, reduce costs, and increase efficiency. However, with the benefits come the substantial responsibility of securing data in the cloud. This blog post delves into enhancing cloud security measures for better protection, a critical concern in today's digital era.
Understanding Cloud Security
Cloud security encompasses the technologies, policies, controls, and services that protect cloud data, applications, and infrastructure from threats. Let’s begin by understanding why cloud security is paramount:
- Data Protection: Ensuring that data stored on cloud servers is protected against unauthorized access, tampering, or theft.
- Compliance: Adhering to industry regulations and data protection laws to prevent legal repercussions.
- Business Continuity: Safeguarding operations against disruptions that could arise from security breaches.
Key Security Measures in Cloud Computing
Here are some core security measures to bolster protection in cloud environments:
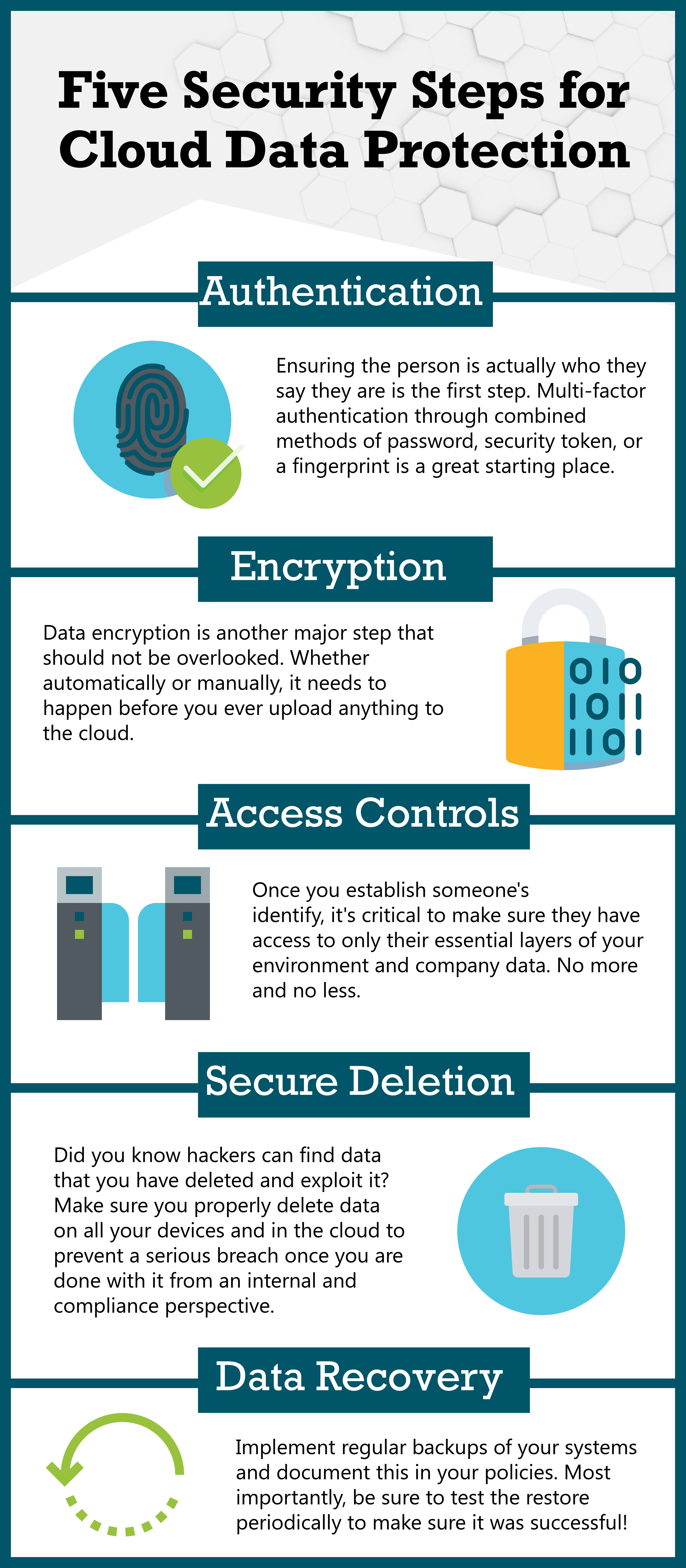
- Identity and Access Management (IAM): Controls who has access to what resources, ensuring that only authorized users can interact with sensitive data.
- Encryption: Utilizing encryption for data at rest and in transit to prevent interception and unauthorized access.
- Data Backup and Recovery: Implementing robust backup and recovery strategies to mitigate data loss in case of disasters.
- Security Audits and Compliance: Regularly conducting security audits and ensuring compliance with standards like ISO 27001 or NIST.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Systems that monitor network traffic for suspicious activities, thus preventing attacks.
- Cloud Access Security Brokers (CASB): Intermediaries that enforce security policies between cloud service users and providers.
Implementing Identity and Access Management
IAM is crucial for securing cloud environments:
- Principle of Least Privilege: Assign the minimum level of access rights necessary for an individual to perform their job.
- Multi-factor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to add an extra layer of security beyond just usernames and passwords.
- Access Reviews: Regularly review and adjust user access rights to prevent over-provisioning or under-provisioning of permissions.
🔐 Note: Continuous monitoring of user activities can help detect and prevent unauthorized access in real-time.
Encryption in Cloud Services
Encryption serves as the bedrock of cloud security:
- Data at Rest: Encrypt sensitive data stored in the cloud with methods like AES-256.
- Data in Transit: Use secure protocols such as HTTPS or TLS to encrypt data while moving through the network.
Furthermore, key management becomes paramount:
- Develop a robust key management policy to control encryption keys' lifecycle, from generation to destruction.

| Type of Data | Encryption Method |
|---|---|
| At Rest | AES-256, RSA |
| In Transit | HTTPS, TLS |
Backup and Recovery
Business continuity hinges on effective backup and recovery solutions:
- Regular Backups: Schedule automatic backups to ensure data is preserved.
- Redundancy: Store backup data in different locations to prevent data loss from disasters.
- Versioning: Keep multiple versions of data to revert to a specific point in time if necessary.
After explaining how to safeguard your cloud environment, here are some important points to note:
⏳ Note: Test your recovery processes frequently to ensure they work as expected during an actual crisis.
Security Audits and Compliance
Audits and compliance help ensure the security infrastructure meets industry standards:
- Audit Logs: Maintain comprehensive logs of all cloud activities for forensic analysis.
- Vulnerability Scanning: Use tools to identify and address security vulnerabilities.
- Penetration Testing: Conduct regular penetration tests to find weaknesses in your cloud setup.
Intrusion Detection and Prevention
IDPS can greatly enhance cloud security:
- Signature-based Detection: Identifies attacks using predefined signatures.
- Anomaly-based Detection: Monitors for unusual behavior that might indicate an attack.
Cloud Access Security Brokers
CASBs act as gatekeepers to the cloud:
- Visibility: Gain visibility into cloud usage to enforce security policies uniformly.
- Compliance: Ensure adherence to regulatory standards by monitoring and reporting on compliance.
Implementing these measures in a cohesive manner will fortify your cloud environment against threats. Here's how to tie everything together:
- Holistic Security Strategy: Develop a comprehensive strategy that encompasses all the above measures.
- Continuous Improvement: Cloud security should evolve continuously as new threats emerge and cloud technologies advance.
In this constantly evolving landscape, securing your cloud resources requires vigilance, advanced tools, and a proactive approach. By understanding and implementing these key security measures, you're not just safeguarding your data but also ensuring the resilience of your business operations.
Why is identity and access management crucial for cloud security?
+IAM is vital as it controls who has access to your cloud resources, ensuring that only authorized personnel can interact with sensitive data, thus reducing the risk of insider threats or unauthorized access.
How does encryption help in securing cloud data?
+Encryption transforms readable data into an encoded version that can only be accessed with a decryption key, thus preventing unauthorized parties from accessing or tampering with the data.
What are the advantages of using a Cloud Access Security Broker?
+CASBs provide enhanced visibility into cloud usage, enforce security policies, detect threats, and ensure compliance with regulatory standards, thereby safeguarding cloud applications and data.
Related Terms:
- cloud security strategies
- enhanced cloud security
- cloud security management plan
- cloud security best practices
- cloud based data encryption
- cloud based security strategy