Cloud Computing Network Security: Essential Insights for Protection

In today's digital landscape, cloud computing has become an integral part of many businesses, offering scalability, flexibility, and cost savings. However, with these benefits come significant security challenges. Understanding and implementing robust network security measures within cloud environments is crucial for protecting sensitive data and ensuring business continuity. This post delves into essential insights for safeguarding your cloud infrastructure.
Understanding Cloud Network Security

Cloud network security involves securing cloud-based services and infrastructure against cyber threats like data breaches, denial of service (DoS) attacks, and unauthorized access. Here's how to approach it:
- Shared Responsibility Model: Recognize that security in cloud computing is a shared effort. Cloud service providers secure the infrastructure (like the physical security of data centers), while clients are responsible for securing their data, applications, operating systems, and network traffic.
- Zero Trust Architecture: Adopt a zero-trust approach, where every user or device trying to access resources must be verified, regardless of their location within or outside the network.
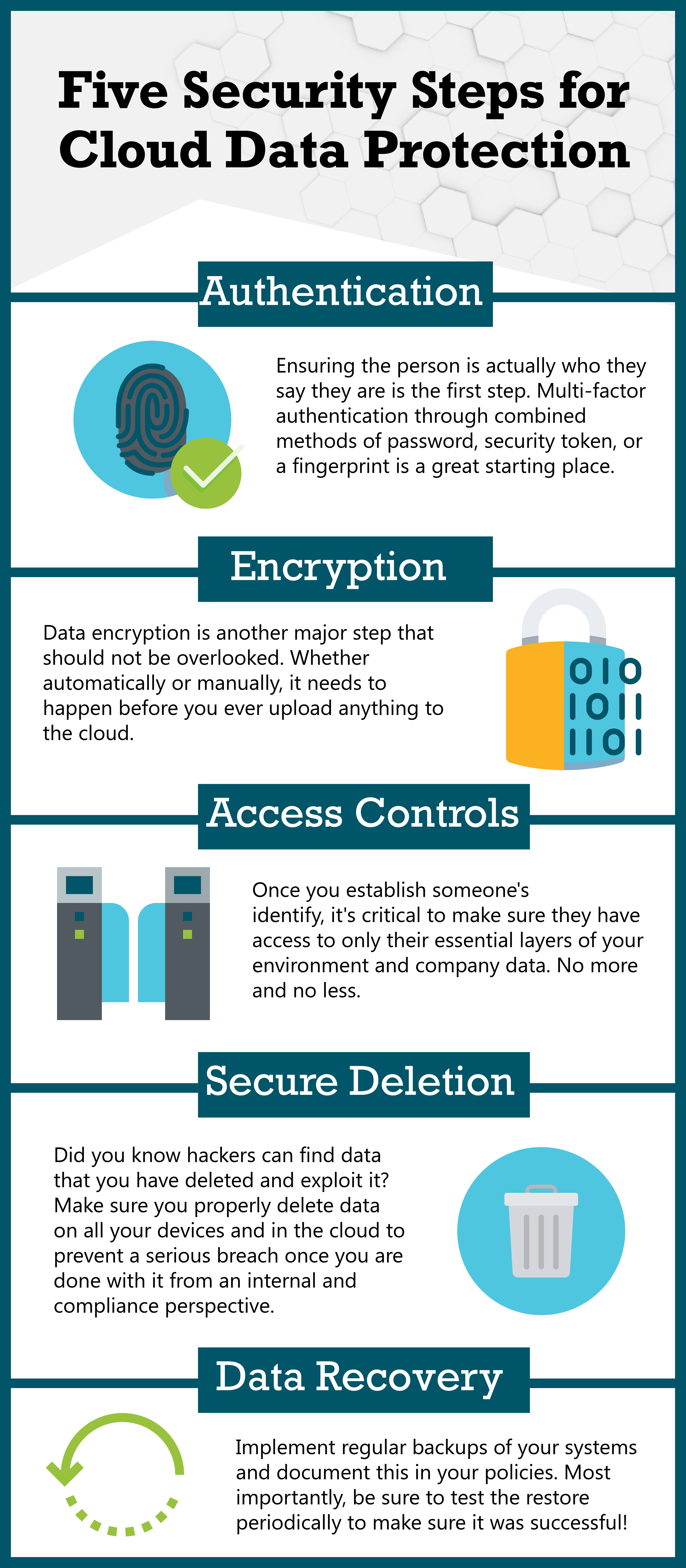
- Encryption: Data should be encrypted both in transit and at rest. Utilize protocols like Transport Layer Security (TLS) for data in transit and AES for data at rest.
Steps to Secure Cloud Networks
1. Identity and Access Management (IAM)
Effective IAM is key to securing cloud networks:
- Multifactor Authentication (MFA): Implement MFA to provide an extra layer of security, ensuring that even if credentials are compromised, unauthorized access is still prevented.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Define access rights based on roles, reducing the attack surface by limiting permissions to what users require for their tasks.
- Regular Audits: Conduct audits to review and revoke unnecessary access rights, ensuring users have access only to what they need.
2. Network Security Measures
Here are some critical network security steps:
- Firewalls: Use firewalls like AWS Security Groups or Azure Network Security Groups to control inbound and outbound traffic.
- Virtual Private Clouds (VPCs): VPCs help isolate your cloud environment from the public internet, reducing the risk of attack.
- Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDPS): Deploy these systems to monitor network traffic and block or alert on suspicious activities.
3. Monitoring and Logging
Continuous monitoring and logging are essential:
- Implement logging solutions like AWS CloudTrail or Azure Monitor to keep track of all user and resource activities.
- Use Security Information and Event Management (SIEM) tools for real-time analysis of logs to detect security anomalies and respond promptly.
4. Vulnerability Management
Vulnerabilities must be identified and mitigated:
- Regularly scan your cloud resources for vulnerabilities using automated tools like Qualys or Nessus.
- Keep your software and systems updated to patch known vulnerabilities.
5. Backup and Disaster Recovery
Establish robust backup and disaster recovery plans:
- Regular backups are crucial; ensure they are stored in a different region or with a third-party provider.
- Create and test a disaster recovery strategy to ensure business continuity in the event of a security breach or failure.
❗️ Note: While cloud providers offer security tools, you are still responsible for managing and configuring these tools properly to ensure your data's protection.
Securing cloud networks involves a multi-layered approach. By understanding the shared responsibility model, implementing strong IAM practices, securing network perimeters, monitoring activities, managing vulnerabilities, and having robust backup and disaster recovery plans, organizations can safeguard their cloud environments effectively. Keeping pace with evolving threats requires ongoing vigilance and the integration of advanced security technologies and practices.
What is the shared responsibility model in cloud security?
+The shared responsibility model divides security duties between cloud service providers and customers. Providers secure the underlying infrastructure, while customers are responsible for securing their data, applications, and certain configurations within the cloud.
How does encryption help in cloud security?
+Encryption secures data by encoding it in a way that only authorized parties can decode and understand it. It protects data both while it’s moving across networks (in transit) and when it’s stored (at rest), preventing unauthorized access or data breaches.
Why is Identity and Access Management (IAM) important in cloud security?
+IAM is crucial as it ensures that only the right users have access to the right resources at the right time. It helps manage permissions, authentication, and authorization, significantly reducing risks associated with insider threats or compromised accounts.
Related Terms:
- Network security in the cloud
- Cloud computing security controls
- Cloud computing security services
- Network security services
- Accenture cloud computing
- Network infrastructure security