Secure Cloud Computing: Protecting Your Data Online

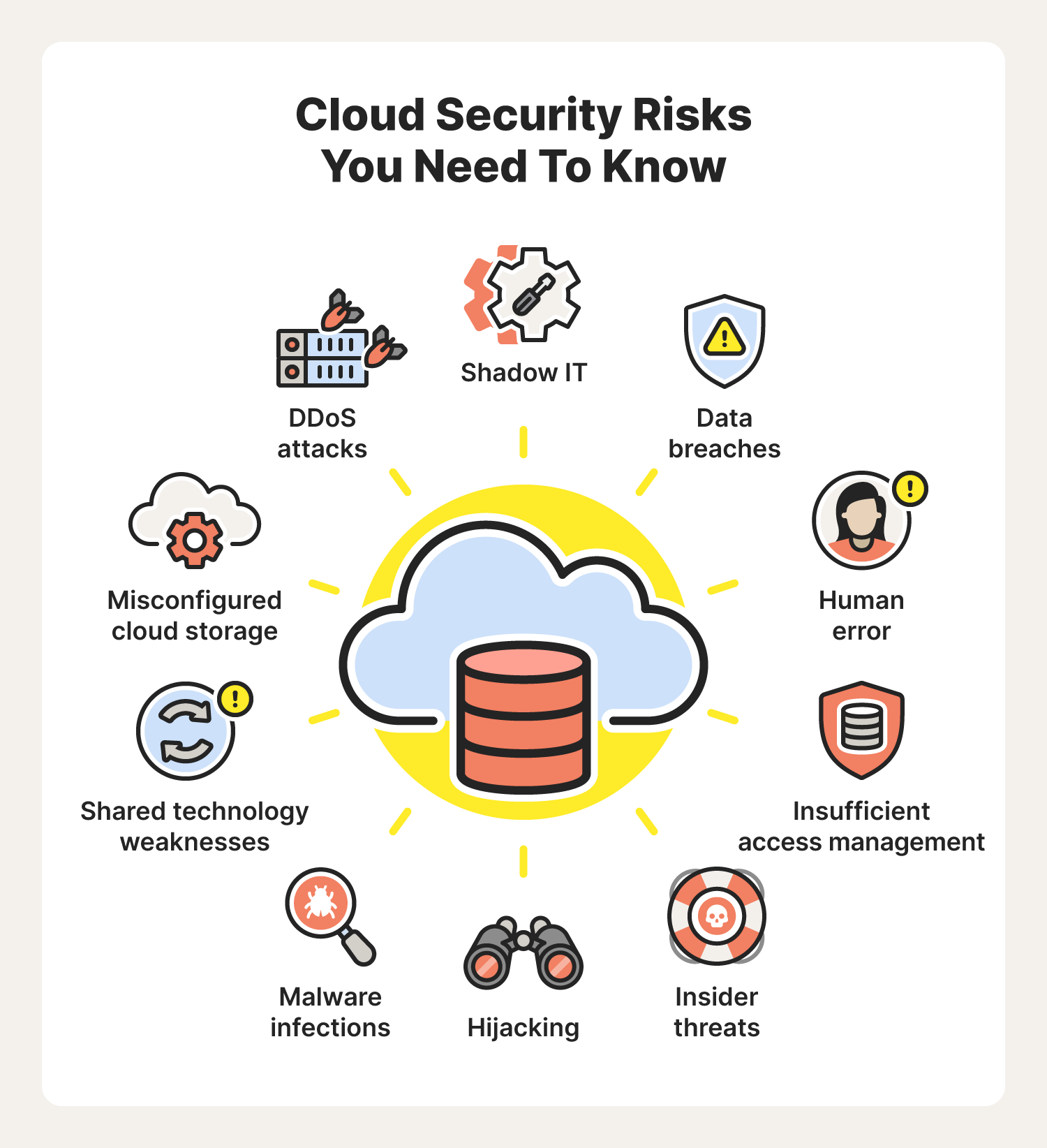
In today's digital age, cloud computing has become an integral part of our lives. It allows us to store, manage, and process data remotely, providing convenience, scalability, and accessibility like never before. However, with these benefits comes the responsibility to secure this data from unauthorized access, breaches, and potential cyber threats. This comprehensive guide will delve into the intricacies of secure cloud computing, providing insights and actionable steps to ensure your data remains private and protected.
Understanding Cloud Security Basics
Cloud computing involves servers, storage, databases, networking, software, analytics, and intelligence over the internet. Here are key aspects you should understand:
- Data Privacy: Ensuring personal information is handled in compliance with legal standards.
- Data Integrity: Protecting data from unauthorized changes.
- Data Availability: Guaranteeing data access when needed.
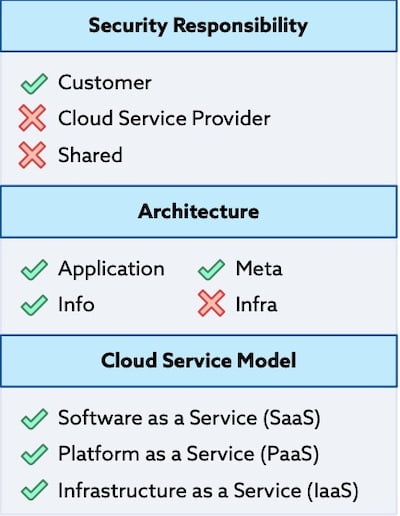
Cloud providers typically offer a shared responsibility model where the cloud provider secures the infrastructure, but the user must secure their data and applications within the cloud.
Choosing the Right Cloud Provider
Selecting the appropriate cloud service provider is the first step towards securing your cloud environment. Consider these criteria:
- Security Certifications: Look for providers with ISO 27001 or SOC 2 compliance.
- Data Encryption: Ensure they provide end-to-end encryption for data at rest and in transit.
- Compliance: Check if the provider meets industry or regulatory standards relevant to your business.
- Redundancy and Backup: Assess their disaster recovery capabilities and data backup options.
💡 Note: While certifications and standards are crucial, they are not an absolute guarantee of security; continuous vigilance is necessary.
Encryption: The First Line of Defense
Encryption is essential for protecting data in the cloud:
- Encryption at Rest: Data stored on disks or storage devices should be encrypted.
- Encryption in Transit: Data should be encrypted as it moves between your device and the cloud.
Using protocols like TLS (Transport Layer Security) or encrypting data with strong algorithms like AES-256 ensures that even if data is intercepted, it’s unreadable without the keys.
🔒 Note: Remember to manage encryption keys properly, as they are as critical as the data they protect.
Access Control and Identity Management
Implementing strict access control is key:
- Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA): Adds an extra layer of security beyond just passwords.
- Role-Based Access Control (RBAC): Limit access to only what is necessary for each role within your organization.
- Identity Management: Use centralized identity management solutions to control access rights and track user activities.
Network Security Measures
Securing the network layer is crucial for cloud computing:
- Firewalls and IDS/IPS: Deploy firewalls to block unauthorized access and Intrusion Detection/Prevention Systems to monitor network traffic.
- Virtual Private Cloud (VPC): Use VPC to isolate your cloud resources within their own private network.
- Virtual Private Network (VPN): Ensure secure remote access using VPNs to create a secure tunnel between your device and the cloud.
A well-designed network architecture not only protects your cloud environment but also helps in meeting compliance requirements.
Monitoring, Auditing, and Incident Response
Continuous monitoring and swift incident response are critical:
- Real-time Monitoring: Use tools that provide real-time alerts for unusual activities.
- Log Analysis: Analyze logs to detect potential security breaches or suspicious behavior.
- Incident Response Plan: Have a plan for detecting, responding to, and recovering from security incidents.
Establish protocols for regular security audits to ensure all security measures are functioning correctly and to update them in response to new threats.
Regulatory Compliance and Legal Considerations
Compliance with legal standards is not just about avoiding penalties but also about building trust:
- GDPR, HIPAA, PCI-DSS: Ensure your cloud strategy complies with data protection laws relevant to your industry or location.
- Data Sovereignty: Understand where your data is stored and which legal jurisdictions it falls under.
Adopting a cloud service provider that supports compliance with various regulations can streamline these requirements.
The Final Step: Security Culture
Protecting your data in the cloud goes beyond technical measures. Here are some practices to foster a security-focused culture:
- Employee Training: Regularly educate your workforce on security best practices and threats.
- Continuous Education: Stay updated with the latest in cloud security to adapt your strategies.
- Encouragement of Reporting: Promote a culture where employees feel comfortable reporting potential security issues.
Security is not just the IT department’s responsibility but a collective effort across the organization.
In conclusion, securing your data in the cloud is an ongoing journey that requires a multi-faceted approach. From selecting a reputable cloud provider to implementing strong encryption and network security measures, every step counts. Remember, cloud security is as much about understanding the technology as it is about fostering a security-conscious culture within your organization. Continuous vigilance, regular updates to security protocols, and adapting to new threats will help ensure your data remains safe in the digital cloud.
Why should I encrypt my data in the cloud?
+
Encrypting data in the cloud ensures that even if someone gains unauthorized access, the data remains unreadable without the encryption keys. It protects data at rest and in transit from being compromised.
What are the benefits of using Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)?
+
MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring more than one form of verification to access your cloud resources, significantly reducing the risk of unauthorized access due to stolen passwords.
How often should I perform security audits in my cloud environment?
+
Regular security audits should be conducted at least quarterly, or more frequently if your business experiences changes in regulations, significant infrastructure updates, or known vulnerabilities in your system.
Related Terms:
- Principle of least privilege
- Data lifecycle policies
- How to secure the cloud
- secure cloud computing pdf
- most secure cloud computing service
- cloud based hosting services security